The 5G rollout brought revolution in the way we connect, stream and communicate. But even before 5G vs 6G reaching every corner of the, the Tech world is discussing about its successor -6G. With promises of faster speed, near-zero delay and smarter connectivity, 6G is expected to reopen the digital future. But how does it really differ from 5G, and what does it mean to consumers, businesses and governments?
Understanding 5G: The Present Standard

The 5G, or fifth generation mobile network began to roll commercially around 2019-2020. By 2025, it has become standard in many urban areas around the world including India.
It brought: Download speed up to 10 GBPS Low delay (~ 1 millisecond) Large scale IOT connectivity Support for real -time applications such as AR/VR, autonomous vehicles and distance surgery But while 5G unlocked smart cities more viable and new consumer technical experiences, its full capacity is still being tapped.
Enter 6G: The Next Leap

6G is expected to roll out commercially around 2030, which aims to take digital communication in a new dimension – both literal and rhetorical. Research and preliminary tests have already begun in countries like South Korea, America, China and Finland.
Major features of 6G:
- Speed up to 1 terabity per second (TBPS) –
- about 100 times faster than 5G Ultra-Lo Letty (<0.1 milliseconds)
- AI-Ug Network
- Integration of satellites and terrestrial networks Holographic Communication
- 6G-Inaculated Smart Wearbals, and Extended Reality (XR)
5G vs 6G: Should You Wait for 6G or Invest in 5G Now?
While 6G promises the abilities to leave the jaw, it is still several years away from the commercial rollout. For now, 5G is the most practical and widely available technology, especially in urban areas of India and other parts of the world. If you are thinking a consumer or business whether to upgrade to 5G devices or wait for 6G – then the answer is clear: go for 5G. It already supports advanced features like cloud gaming, high-definition video calling and real-time smart application. When 6G reaches, most 5G networks and devices will continue to work during the transition period.
5G vs 6G: Core Differences
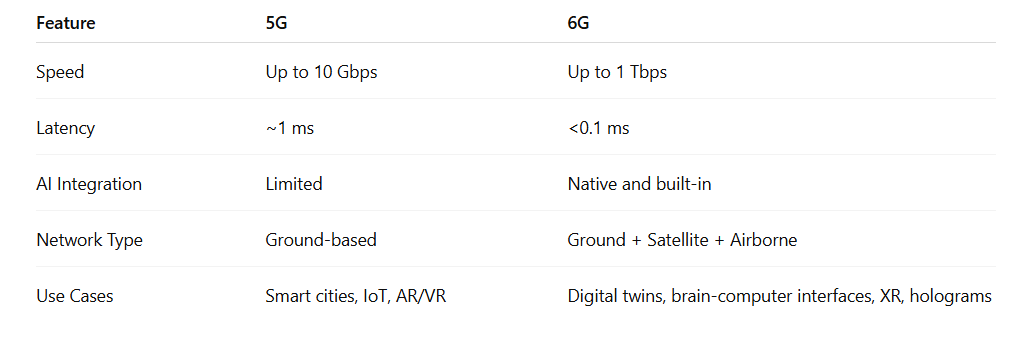
5G vs 6G: Challenges to Global Adoption
While 6G promises are exciting, important obstacles are:
- High growth and signs cost
- Global standardization issues
- Privacy and cyber security threats
- Environment and electricity consumption concerns
- 5G vs 6G: Should You Wait for 6G or Invest in 5G Now?
Conclusion: 5G vs 6G – The Evolution of Mobile Networks
5G continues to increase our digital life, but 6G is already designed to support which comes forward. The innings from 5G to 6G will not only be about rapid data – it will be about intelligent, responsible and uninterrupted communication worldwide. The 5G vs. 6G race is not just a technical competition – it is a preview of how humanity will be connected in the next decade.
Also Read : How Chatgpt Increased Business Users By 50% In Six Months
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the main difference between 5G and 6G?
The main difference is in speed and intelligence. 5G offers speeds up to 10 Gbps, while 6G is expected to reach 1 Tbps. 6G will also integrate AI natively and support more advanced technologies like holograms, digital twins, and brain-computer interfaces.
2. When will 6G be available in India?
6G is expected to launch globally around 2030. Research and pilot projects may begin in India around 2026–2027, but widespread commercial use is likely after 2030.
3. Will 6G replace 5G completely?
Not immediately. Like past generations, 6G will co-exist with 5G for several years. Devices and networks will likely support both technologies during the transition phase.
4. Is 6G harmful to health?
As of now, there is no scientific evidence proving that 5G or 6G frequencies are harmful to human health. However, international health organizations continue to study long-term exposure effects.
5. How fast will 6G be compared to 5G?
6G will be up to 100 times faster than 5G. While 5G can offer speeds of up to 10 Gbps, 6G aims to deliver up to 1 Terabit per second (Tbps) under ideal conditions.











